Annuity Factor
The annuity factor definition is the use of a financial method that shows the value, present or future, of an amount when it is multiplied by a periodic amount. The calculation of an annuity factor requires the number of years involved, or the periodic amount, and the percentage rate applicable. The most often used for annuity factors are investments with either or both an annual payment or return. Typical examples of annuity factors being applied are savings accounts, certain types of insurances, or retirement savings plans.
The annuity factor meaning is a particular type of accumulating discount factor used to determine the present or future value of annuities, as well as equated installments. Another name for annuity factors is the annuity formula, and we’ll get into that momentarily.
The Present Value Annuity Factor
The present value annuity factor allows you to determine the amount of money required at the present time in order to result in a future series of payments assuming a fixed interest rate is applied.
In order to reach the present value annuity factor, a formula is used that discounts a future value amount to the present value amount through the use of the applicable interest rate. The period of time during which the investment will last is also taken into account to reach the correct value.
The Present Value Annuity Formula
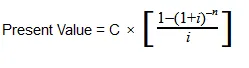
With:
C=cash flow per period
i = interest rate
n = number of payments
The Future Value Annuity Factor
The future value annuity factor gives access to the final return value of a series of regular investments taking into account their worth at a future time, usually at the end of the investing period, assuming that a fixed interest rate is applied.
To reach the future value annuity factor, the formula above is slightly altered in order to add the values collected over the years by also accounting for the set interest rate.
The Future Value Annuity Factor
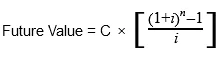
With:
C=cash flow per period
i = interest rate
n = number of payments
Applying the Annuity Factor formulas:
Considering an investment with an annual $2,000 payment over the course of five years at an interest rate of 5%, let’s see what the present and future value would be.
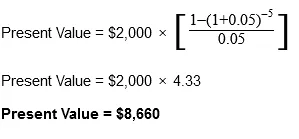
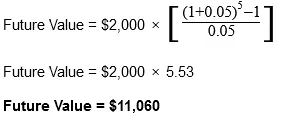
The previous formulas can help you determine the present and future values of ordinary annuities. While the math might seem complicated, there are financial calculators online that can help you out with the correct inputs and data.
Popular Real Estate Terms
Founded in 1947 and located in Washington, DC, the NAREB has 7,500 members with 15 regional groups and 6 state groups. It offers certification programs for members of the real estate ...
An interim or provisional court decree, which is not final and can be reversed or amended, normally issued to direct additional proceedings prior to issuing a final decree. For example, an ...
Supervisor of the operation of apartments while residing in one of the apartments. Some responsibilities include showing vacant apartment to prospective tenants and assuring that the ...
North-south lines that encircle the earth and used as references in mapping land. ...
Federal tax legislation notably establishing 10% withholding on interest and dividends. ...
Conversion of a rental apartment house to individual condominium ownership of a portion of the minimum ownership of a portion of the building. Often, the tenant is given an opportunity to ...
An offering of securities, stock and/or debt, directly to investors rather then through the public exchange markets. An advantage of a private placement to a real estate business is that ...
The term effective interest rate is the actual return from a savings account or any investment where you pay interest when considering the effects of compounding costs over time. Through an ...
Annual Percentage Rate (APR) is a measure of the cost of credit that must be reported by lenders under the Truth in Lending regulations. The Annual Percentage Rate (APR) takes into ...
Have a question or comment?
We're here to help.