Effective Interest Rate
The term effective interest rate is the actual return from a savings account or any investment where you pay interest when considering the effects of compounding costs over time. Through an effective interest rate, you can fully and correctly determine the real percentage rate that you own on a loan’s interest, a credit card, or any other debt type.
An effective interest rate is also referred to as an effective annual interest rate, the annual equivalent rate, or the effective rate.
The Effective Interest Rate Formula:
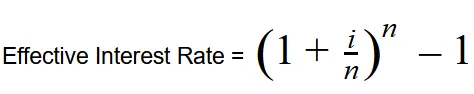
With:
i = Nominal Interest Rate
n = Number of periods
What does the Effective Interest Rate Mean?
When you look at loans, the way through which they are advertised will give you two types of information. Firstly, we’ll have the nominal interest rate, which doesn’t consider the effects compounding interest or fees have on the financial product. Secondly, and the one we focus on now, the effective interest rate, which gives you the real return paid on savings of the actual cost of a loan because it does take into account the effect fees and compounding interest have on the financial product.
For that exact reason, knowing and understanding what the effective interest rate means is important. Through a proper understanding of the effective interest rate, you can compare offers more accurately to make an informed decision based on the result.
How to Find the Effective Interest Rate?
To adequately explain how to find the effective interest rate from any financial product’s promotional information, we will look at two examples. Firstly, we’ll have Loan A that has a 5% interest rate that’s compounded monthly. Secondly, we’ll have Loan B with a 5.1% interest rate that’s compounded bi-annually.
Both of these loans are advertised with their nominal interest rate. Remember, this is the one that doesn’t take into account the effects fees and compounding interest has on the loan. To calculate the effective interest rate, we’ll use the formula shown above.
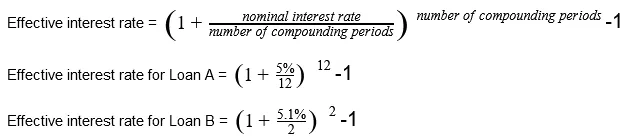
While the nominal interest rate for Loan A is smaller than that of Loan B’s, the effective interest rate from Loan B is lower than that of Loan A’s. This occurs because Loan B has fewer compounding times over the course of a year.
Popular Real Estate Terms
Changing property ownership. An example is the sale of a home to another. ...
A lender can be a private individual, a private or public group, or an institution that loans funds to a person or business that the lendee would later repay with interest in most cases. In ...
The definition of real estate owned (REO) is known by heart by house flippers or by real estate agents specialized in bank owned properties. These are properties that once used to be in a ...
Provision permitting a lender to charge the borrower a penalty for repaying a loan before its due date. ...
Housing where affirmative action is proactively pursued protecting the housing rights of people of all races, nationalities, and religions. ...
Insurance based on the National Flood Insurance Program, enacted By Congress in 1968. The intent of this legislation is to provide insurance coverage for those people suffering real ...
Individual renting a residential or office unit. ...
In order to define allotment, we have to take into consideration what it refers to. While generally, it refers to a certain amount of something that is allocated to a particular person, the ...
Something that is illegal. An example is an unenforceable debt because it has exceeded the statute of limitations. ...
Have a question or comment?
We're here to help.