Mortgage Amortization
The term mortgage amortization is the steady switch occurring to each mortgage payment between how much interest is covered and how much principal each month. Simply put, mortgage amortization is the plan for repaying a mortgage. Because the debt diminishes with each payment, the interest diminishes, and because the interest decreases monthly, the principal coverage increases with each payment.
The Mortgage Amortization Definition
Amortization is the way through which mortgages are repaid. This feature can be applied to mortgages with an equal monthly payment and a fixed timeline. Mortgages, as well as other loans, can be amortized.
Let’s see this through a more practical explanation. The trademark of an amortized mortgage or amortized loan is the shift from paying mostly interest every month to mainly paying principal every month. The math goes like this: for a $100,000 mortgage with a 4.5% interest rate, amortized over a span of 30 years, the fixed monthly payment totals at $507. In this value, during the first month, we will see that $375 goes to cover the interest, and the remaining $132 covers the principle. Towards the mortgage’s mid-term, there is a switch with $249 going to the interest and $257 to the principle. The last mortgage payment will be split into $2 for the interest and $505 for the principal.
How does Mortgage Amortization work?
Mortgage amortization is a repayment plan that uses an amortization table or amortization schedule as a way to visualize the concept. An amortization schedule is a grid or table showing how payments are split between the interest and the principal, and the balance that remains after each payment. Below you can see how mortgage amortization works in time.
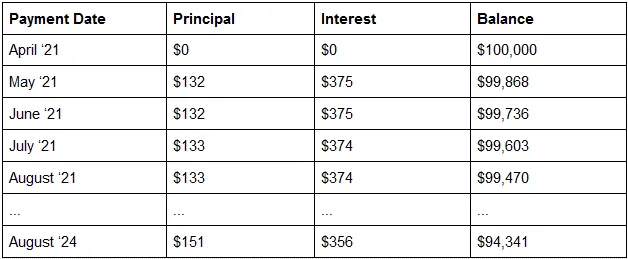
With mortgage amortization, after four payments, the balance reaches $99,470, and in 3 years, the balance is $94,341. An amortized mortgage is a loan where the balance decreases gradually at first and more abruptly in the final years. Similarly, equity is built slowly at first but more rapidly in the last years.
Popular Real Estate Terms
The two terms used to describe professionals in the real estate industry are “realtor” and “real estate agent”. These two terms are used interchangeably or as ...
Generally, the term turnover is the accounting method of calculating how fast operations are conducted by a business. The simplest turnover definition is the rate at which a company sells ...
Something that is of good value for the money and an attractive deal. ...
The definition of a storm ready community is any community across the country that demonstrates it has the means to prepare and educate the population for severe weather conditions. ...
The definition of an absentee owner is a property owner who does not reside on the property. An absentee can be an individual or a corporation with legal ownership over a property ...
Expenditures incurred to develop real estate. An example is the cost to build a shopping center. ...
Court order granted in favor of the landlord to remove a tenant from the property because of nonpayment of rent and/or damaging the property. The writ directs an officer of the law to ...
Character defines as a set of qualities that set apart a person, place, or object from others. When it comes to people, a character describes moral qualities and personality traits that ...
Among other things. Inter alia is an ancient method of referring to statutes without reciting all of their provisions. ...

Have a question or comment?
We're here to help.